 | James Hodgson - Astronomy - 1723 - 724 pages
...t,¿z¿xct,í7<r— Axes, bac; that is the Radius multiplied into the Sine of the Complement of the Angle a or Sine of the Middle Part, is equal to the Product of the Tangent of ab one of the Extreams, into the Tangent of the Complement of л с the other Extream. By... | |
 | Euclid, John Keill - Geometry - 1733 - 444 pages
...S, CF=Cof. BC and T, DF = Cot. B. Wherefore R x Cof. BC=Cot. Cx Cot. B ; that is, Radius drawn into the Sine of the. middle Part, is equal to the Product of the Tangents of the adjacent extreme Parts. : X And And BA, AC, are the oppofite Extremes to the faid middle Part, viz.... | |
 | David Stewart Erskine Earl of Buchan, Walter Minto - Logarithms - 1787 - 164 pages
...fpherical triangle, The product of the tangents of half the fum and half the difference of the fegments of the middle part is equal to the product of the tangents of half the fum and half the difference of the oppofite parts. Dem. For fince cof BA: cof BC :: cof DA:... | |
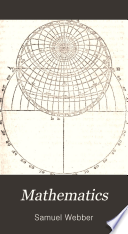 | Mathematics - 1801 - 658 pages
...solutions of all the cases of right-angled spherical triangles. THEOREM VII. The product of radius and the sine of the middle part is equal to the product of the tangents of the conjunct extremes, or to that of the cosines of the disjunct extremes.* NOTE. * DEMONSTRATION. This... | |
 | Thomas Kerigan - Nautical astronomy - 1828 - 776 pages
...part, is equal to the product of the tangents of the extremes conjunct2d. — The product of radius and the sine of the middle part, is equal to the product of the co-sines of the extremes disjunct. Since these equations are adapted to the complements of the hypotheiiuse... | |
 | Benjamin Peirce - Spherical trigonometry - 1836 - 92 pages
...sine of the middle part is equal to the product of the tangents of the two adjacent parts. (475) II. The sine of the middle part is equal to the product of the cosines of the two opposite parts. Demonstration. To demonstrate the preceding rules, it is only necessary... | |
 | Thomas Kerigan - Nautical astronomy - 1838 - 804 pages
...is equal to the product of the tangents of the extremes conjunct. 2d. — Tlie product of radius and the sine of the middle part, is equal to the product of the co- sines of the extremes disjunct. Since these equations are adapted to the complements of the hypothenuse... | |
 | Henry W. Jeans - Trigonometry - 1842 - 138 pages
...of the middle part is equal to the product of the tangents of the two parts adjacent to it. RULE II. The sine of the middle part is equal to the product of the cosines of the two parts opposite to, or separated from it. Having written down the equation according... | |
 | Benjamin Peirce - Plane trigonometry - 1845 - 498 pages
...middle part is equal to Ike product of the tangents of the two adjacent parts. Napier's Rules. II. The sine of the middle part is equal to the product of the cosines of the two opposite parts. [B. p. 436.] Proof. To demonstrate the preceding rules, it is only... | |
 | Benjamin Peirce - Plane trigonometry - 1845 - 498 pages
...other two parts are called the opposite parts. The two theorems are as follows. Napier's Rules. II. The sine of the middle part is equal to the product of the cosines of the two opposite parts. [B. p. 436.] Proof. To demonstrate the preceding rules, it is only... | |
| |