 | Charles Davies, Adrien Marie Legendre - Geometry - 1885 - 538 pages
...centre. A sphere may be generated by a semicircle revolving about its diameter as an axis. 13. A RADIU8 of a sphere is a straight line drawn from the centre to any point of the surface. A DIAMETER is a straight line through the centre, limited by the surface.... | |
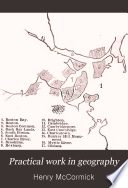 | Henry McCormick - Geography - 1885 - 424 pages
...fixed point. Is it necessary in this definition to say that the "fixed point" must be within ? Why ? The radius of a sphere is a straight line drawn from the center to any point in the surface. The diameter of a sphere is a straight line drawn through the center... | |
 | Webster Wells - Geometry - 1886 - 392 pages
...curved surface, all •points of which are equally distant from a point within called the centre. A radius of a sphere is a straight line drawn from the centre to the surface, and a diameter is a straight line drawn through the centre, having its extremities in... | |
 | Edward Albert Bowser - Geometry - 1890 - 420 pages
...sphere may be generated by the revolution of a semicircle ACB about its diameter AB as an axis. 658. A radius of a sphere is a straight line drawn from the centre to any point of the surface. A diameter of a sphere is a straight line passing through its centre, and... | |
 | Horatio Nelson Robinson - Arithmetic - 1892 - 428 pages
...straight line passing through the center of the sphere, and terminated at both ends by its surface. 548. The Radius of a sphere is a straight line drawn from the center to any point in the surface. EXAMPLES. 549. To find the convex surface of a regular pyramid... | |
 | Horatio Nelson Robinson - Arithmetic - 1892 - 428 pages
...straight line passing through the center of the sphere, and terminated at both ends by its surface. 548. The Radius of a sphere is a straight line drawn from the center to any point in the surface. EXAMPLES. 549. To find the convex surface of a pyramid or cone.... | |
 | Henry B. Maglathlin - 1894 - 370 pages
...curved surface, all points of which are equally -rx distant from a point within called the center. 429. The RADIUS of a sphere is a straight line drawn from the center to any point in the surface. 430. The DIAMETER of a sphere is a straight line drawn through... | |
 | Horatio Nelson Robinson - Arithmetic - 1895 - 526 pages
...straight line passing through the center of the sphere, and terminated at both ends by its surface. 920. The Radius of a sphere is a straight line drawn from the center to any point in the surface. Examples. 921. To find the surface of a sphere. 1. Find the surface... | |
 | George Albert Wentworth - Geometry, Solid - 1899 - 246 pages
...may be generated by the revolution of a semicircle ACB about its diameter AB as an axis. 739. DEF. A radius of a sphere is a straight line drawn from the centre to the surface. A diameter of a sphere is a straight line passing through the centre and limited by the... | |
 | William Taylor Campbell - Geometry - 1899 - 276 pages
...curved, and all parts of it are equally distant from a point within the sphere, which is the centre. A radius of a sphere is a straight line drawn from the centre to the surface. A diameter of a sphere is a straight line drawn through the centre and bounded at each... | |
| |