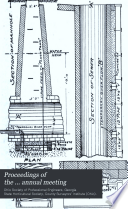
 | Engineering - 1896 - 742 pages
...adding 10 to its characteristic. Theorem I. The square on any side of a triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, minus twice the product of these sides into the cosine of their included angle. First, if the angle B is acute we have b2=a2+c2 —... | |
 | Andrew Wheeler Phillips, Irving Fisher - Geometry, Modern - 1896 - 276 pages
...THEOREM 325. In any triangle, the square of the side opposite an acute angle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, minus twice the product of one of these sides and the projection of the other side upon it. a, FIG. i n FIG. a GIVEN the triangle... | |
 | Andrew Wheeler Phillips, Irving Fisher - Geometry - 1896 - 554 pages
...THEOREM 325. In any triangle, the square of the side opposite an acute angle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, minus twice the product of one of these sides and the projection of the other side upon it. a no. t n FIG. • GIVEN the triangle... | |
 | George D. Pettee - Geometry, Modern - 1896 - 272 pages
...XII 263. Theorem. In any triangle the square of a side opposite an acute angle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides minus twice the product of one of these sides and the projection of the other upon it. D Appl. Cons. Dem. F'o. 1. FIG. 2. Prove... | |
 | University of the South - 1896 - 148 pages
...rhombus. (5) In any triangle the square of the side opposite an acute angle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, minus twice the product of one of these sides into the projection of the other side upon it. IV. LATIN. Sight reading: Cicero... | |
 | James William Nicholson - Trigonometry - 1898 - 204 pages
...the following is the 56 Translation: The square of any side of any triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, minus twice the product of these sides into the cosine of their included angle. While all other trigonometric relations of the sides... | |
 | Webster Wells - Geometry - 1898 - 250 pages
...THEOREM 277. In any triangle, the square of the side opposite an acute angle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, minus twice the product of one of these sides and the projection of the other side upon it. D B fig. 1. Fig. 2. D Given C an acute... | |
 | Mathematics - 1898 - 228 pages
...straight lines. 3. In any triangle the square of the side opposite an acute angle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, minus twice the product of one of these sides and the projection of the other side upon it. 4. State and prove the theorem for... | |
 | Daniel Alexander Murray - Plane trigonometry - 1899 - 350 pages
...like manner, or can be obtained from (3) by symmetry : 62 = c2 + a2-2cacos.B, i? = a2 + b*-2abcosC. (3') These formulas can be expressed in words : In...the square of any side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides minus twice the product of these two sides multiplied by the cosine... | |
 | Webster Wells - Geometry - 1899 - 450 pages
...THEOREM 277. In any triangle, the square of the side opposite an acute angle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, minus twice the product of one of these sides and the projection of the other side upon it. D Fig. 1. B Given C an acute Z of... | |
| |