 | Charles Hutton - Mathematics - 1811 - 404 pages
...measure of ACE, supposing there to be • known АРБ = p, UPC = p, CP =: d, BC = L, AC = R. Since the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles (th. 16 Geom.), we have, with respect to the triangle IAP, AIB = p... | |
 | Charles Hutton - Mathematics - 1812 - 624 pages
...c, the measure of ACB, supposing there to be known APB = r, BPC =fi, CP = d, BC = L, AC = R. Since the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles (th. 1 6 Geom.), we have, •with respect to the triangle IAP, AIB... | |
 | John Gummere - Surveying - 1814 - 398 pages
...took the angle of elevation BAG = 26° 30'. Required the height of the tree. Calculation. 1. Because the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two interior and opposite ones, the angle BDC = DAC + ACD ; therefore ACD - BDC — DAG = 25°... | |
 | Olinthus Gregory - Plane trigonometry - 1816 - 278 pages
...the measure of ACB, supposing there to be known c , APB = P, BPC = p, CP = d, BC = -LI AC = B. Since the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles, we have, with respect- to the triangle IAP, AIB = i> + IAP; and with... | |
 | John Farrar - Logarithms - 1822 - 270 pages
...another distance CB = 60 feet in the same direction, and take the angle ABD = 23° 45'. Now, sinre the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the interior opposite angles, we have that is 4l° — 23° 45' =17° 15'. Hence in the triangle BAC. As sin BAC=... | |
 | Education - 1833 - 414 pages
...to impress on the mind of the pupil that one known fact may be connected with another, so that tiie second, if not known, might have been found out by...opposite angles, then it follows that the angle at the centre of a circle is double of that at the circumference, &c. ; so that the last proposition is proved... | |
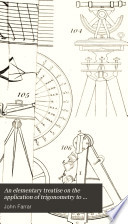 | John Farrar - Trigonometry - 1833 - 274 pages
...another distance CB = 60 feet in the same direction, and take the angle ABD = 23° 45'. Now, since the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the interior opposite angles, we have ACD — A&b = BAC. that is 41° — 23° 45' = 17° 15'. Hence in the triangle... | |
 | John Farrar - Trigonometry - 1833 - 276 pages
...another distance CB = 60 feet in the same direction, and take the angle ABD = 23° 45'. Now, since the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the interior opposite angles, we have ACD — ABC = EAC. that is 41° — 23° 45' = 17° 15'. Hence in the triangle... | |
 | Schoolmaster - 1836 - 926 pages
...other, are first connected as a specimen. For example, suppose it known that the angles at the base ofan isosceles triangle are equal, and also that the exterior...equal to the sum of the interior and opposite angles. Suppose it also indisputable, that if A and B he respectively double of C and D, the sum or difference... | |
 | John Narrien - Geodesy - 1845 - 484 pages
...the angle s' EH is equal to twice the angle AFB or OAF, produce FB to K, and FA to M : then because the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the interior and opposite angles (Euc. 32. 1.), the angle ABK = BAF + AFB; whence 2 ABK = 2 BAF +2 AFB: but the angle of incidence being... | |
| |