 | John Farrar - Logarithms - 1822 - 270 pages
...oblique side CB by the sine of the angle of the parallelogram, radius being unity (Trig. 30). Hence, the area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of any two contiguous sides multiplied by the sine of the contained angle, radius being unity. Given AB = 59 chains... | |
 | John Farrar - Logarithms - 1822 - 244 pages
...oblique side CB by the sine of the angle of the parallelogram, radius being unity (Trig. 30). Hence, the area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of any two contiguous sides multiplied by the sine of the contained angle, radius being unity. Given AB = 59 chains... | |
 | John Farrar - Trigonometry - 1833 - 276 pages
...oblique side CB by the sine of the angle of the parallelogram, radius being unity (Trig. 30). Hence, the area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of any two contiguous sides multiplied by the sine of the contained angle, radius being unity. Given AB = 59 chains... | |
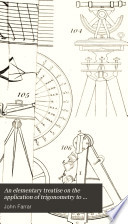 | John Farrar - Trigonometry - 1833 - 274 pages
...oblique side CB by the sine of the angle of the parallelogram, radius being unity ((Trig. 30). Hence, the area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of any two contiguous sides multiplied by the sine of the ( contained angle, radius being unity. Given AB = 59... | |
 | Thomas Tate (mathematical master.) - 1848 - 284 pages
...are understood to mean the number of linear units contained in them. In this sense, therefore, we say that the area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of the base by the perpendicular. As a triangle is one-half the parallelogram having the same base and... | |
 | Thomas Lund - Geometry - 1854 - 520 pages
...measure of the parallelogram ABCD=ABxBE = the base*. the height, as it is usually stated. In other words the area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of any one side and the perpendicular distance of that side from the opposite side. In any proposed case,... | |
 | Charles Davies - Geometry - 1872 - 464 pages
...denote the continued product of the number of linear units in each of the three lines. Thus, when we say that the area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of its base and altitude, we mean that the number of superficial units in the parallelogram is equal to... | |
 | Adrien Marie Legendre - Geometry - 1874 - 500 pages
...the continued product of the number of linear units in each of the three lines. Thus, -when we say that the area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of its base and altitude, we mean that the number of superficial units in the parallelogram is equal to... | |
 | William Guy Peck - Arithmetic - 1877 - 430 pages
...what is its altitude ? Ans. 16 ft. AREA OF A PARALLELOGRAM. 285. It is shown in Geometry (B. 4, P. 3), that the area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of its base and altitude; that is, Area of parallelogram = Base x Altitude. EXAM PLE S. 1. The base of... | |
 | Albert Newton Raub - Arithmetic - 1877 - 348 pages
...following are the rules for the measurements of triangles: It was proved in Denominate Numbers (Art. 107) that the area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of its base and altitude, and since a triangle is half a parallelogram, we derive the following RULE.... | |
| |