 | John Farrar - Logarithms - 1822 - 270 pages
...corresponding oblique side CB by the sine of the angle of the parallelogram, radius being unity (Trig. 30). Hence, the area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of any two contiguous sides multiplied by the sine of the contained angle, radius being unity. Given AB... | |
 | John Farrar - Logarithms - 1822 - 244 pages
...corresponding oblique side CB by the sine of the angle of the parallelogram, radius being unity (Trig. 30). Hence, the area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of any two contiguous sides multiplied by the sine of the contained angle, radius being unity. Given AB... | |
 | Peter Nicholson - Architecture - 1823 - 210 pages
...rectangle is said to be contained by two of its sides, about any one of its angles. THEOREM 52. 147. The area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of its base and altitude. For the parallelogram ABCD is equal to the rectangle ABEF, which has the same base... | |
 | John Farrar - Trigonometry - 1833 - 276 pages
...corresponding oblique side CB by the sine of the angle of the parallelogram, radius being unity (Trig. 30). Hence, the area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of any two contiguous sides multiplied by the sine of the contained angle, radius being unity. Given AB... | |
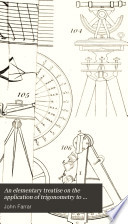 | John Farrar - Trigonometry - 1833 - 274 pages
...corresponding oblique side CB by the sine of the angle of the parallelogram, radius being unity ((Trig. 30). Hence, the area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of any two contiguous sides multiplied by the sine of the ( contained angle, radius being unity. Given... | |
 | John Playfair - Euclid's Elements - 1844 - 338 pages
...any triangle is equal to the product of its base by half its altitude. UOR. 1. Hence, the area of any parallelogram is equal to the product of its base by its altitude. PROP. XXIV. THEOR. The parallelograms about the diameter of any parallelogram, are similar to the whole,... | |
 | Elias Loomis - Conic sections - 1849 - 252 pages
...the base, and the other the number of linear units contained in the altitude. PROPOSITION V. THEOREM. The area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of its base by its altitude. Cor. Parallelograms of the same base are to each other as their altitudes, and parallelograms... | |
 | Adrien Marie Legendre - Geometry - 1852 - 436 pages
...square on a single one ; on a triple line it is nine times as great, &c. E PROPOSITION V. THEOEEM. The area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of its base and altitude. Let ABCD be any parallelogram, and BE its altitude : then will its area be equal... | |
 | Charles Davies - Geometry - 1854 - 436 pages
...the square on a single one ; on a triple line it is nine times as great, &c. PROPOSITION V. THEOREM. The area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of its base and altitude. Let ABCD be any parallelogram, and BE its altitude: then will its area be equal... | |
 | Charles Davies, William Guy Peck - Mathematics - 1855 - 628 pages
...is an equilateral parallelogram or rhojnbus. The diagonals of a rectangle are equal to each other. The area of a parallelogram is equal to the product of its base by its altitude. Any two parallelograms having the same or equal bases are to each other as their altitudes... | |
| |