 | Henry Brougham Baron Brougham and Vaux, Edward John Routh - Physics - 1855 - 540 pages
...force that this motion may be possible. The equiangular spiral, by definition, possesses the property that the tangent at any point makes a constant angle with the radius vector : let this angle be called a. Let r and v be the radius vector and velocity of the particle at any... | |
 | Henry Brougham Baron Brougham and Vaux, Edward John Routh - Physics - 1855 - 512 pages
...force that this motion may be possible. The equiangular spiral, by definition, possesses the property that the tangent at any point makes a constant angle with the radius vector: let this angle be called a. Let T and v be the radius vector and velocity of the particle at any time... | |
 | Edward Tomkins - Machinery - 1878 - 376 pages
...or a number of similar sections may be employed to build up a complete wheel. A logarithmic spiral is a curve such that the tangent at any point makes a constant angle with the radius at that point; the radius being the line drawn from the point on the curve to the centre or pole of... | |
 | De Volson Wood - Geometry, Analytic - 1882 - 360 pages
...071/ ON , progression ; that is, -^=- = -^^ , etc. (J Li UM This curve is called equiangular because the tangent at any point makes a constant angle with the radius vector at that point.* 269. The Involute of a Circle is the locus of any -L point of a line as it rolls upon... | |
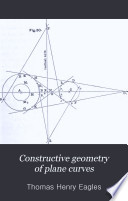 | Thomas Henry Eagles - 1885 - 404 pages
...length of the radius vector, whence it derives its first name; it is called equiangular because in it the tangent at any point makes a constant angle with the radius vector. This constant angle is called the angle of the spiral. The equation to the curve is generally expressed... | |
 | De Volson Wood - Geometry, Analytic - 1890 - 372 pages
.... . OM ON progression ; that is, -.- = -= , etc. FIG. 178. This curve is called equiangular because the tangent at any point makes a constant angle with, the radius vector at that point* 269. The Involute of a Circle is the locus of any point of a line as it rolls upon a... | |
 | Edward Harrington Lockwood - Curves - 1967 - 290 pages
...in any position and the fact characterizes the curve along which a dog moves. Such a curve, in which the tangent at any point makes a constant angle with the radius drawn to that point from a fixed point, is called an equiangular spiral. As the dog at B' is moving... | |
| |