 | Samuel Webber - Mathematics - 1808 - 466 pages
...x A o; but A?2=Ao2+oy2=tAo3, hence Ay 22 and consequently, Ar = AB is the side of the pentagon. As the square of the side of a regular pentagon, inscribed in a circle, is equal to the sum of the squares of the radius and of the side of a regular decagon, inscribed in the same circle,... | |
 | Robert Woodhouse - Geometrical optics - 1819 - 470 pages
...equilateral pentagon and decagon, inscribed in a circle. Hence, the square of the side of an equilateral pentagon inscribed in a circle, is equal to the square of the radius plus the square of the side of an equilateral decagon inscribed in the same circle. Having now... | |
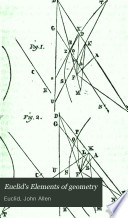 | Rev. John Allen - Astronomy - 1822 - 516 pages
...construction, AB one of the sides of the inscribed hexagon, is equal to the radius AG (Constr.). Cor. 2. — The square of the side of a regular pentagon, inscribed in a circle, is equal to the squares, of the sides of a regular hexagon, and regular decagon, inscribed in the same circle. For... | |
 | Rev. John Allen - Astronomy - 1822 - 508 pages
...construction, AB one of the sides of the inscribed hexagon, is equal to the radius AG (Constr.). Cor. 2.—The square of the side of a regular pentagon, inscribed in a circle, is equal to the squares, of the sides of a regular hexagon, and regular decagon, inscribed in the same circle. For... | |
 | Daniel Cresswell - Euclid's Elements - 1825 - 616 pages
...the sides being taken in order from any one of them assumed as the first. PROP. XVII. 29. THEOREM. The square of the side of a regular pentagon, inscribed in a given circle, is equal to the square of the side of a regular decagon, together with the square of... | |
 | Alfred Wrigley - 1845 - 222 pages
...ratio between the areas of an equilateral triangle and a square inscribed in the same circle. 172. The square of the side of a regular pentagon inscribed in a circle is equal to the sum of the squares of the sides of a regular hexagon and a decagon inscribed in the same circle. 173.... | |
 | Euclides - 1845 - 546 pages
...shew that the angle ECF is a right angle. 3Q. The square described upon the side of a regular pentagon in a circle, is equal to the square of the side of a regular hexagon, together with the square upon the side of a regular decagon in the same circle. 40. From B... | |
 | Euclides - 1850 - 350 pages
...touch respectively the four sides of the square. 77- Inscribe a regular decagon in a given circle. a circle, is equal to the square of the side of a regular hexagon, together vtith the square upon the side of a regular decagon in the same circle. X. 79. In... | |
 | Alfred Wrigley - 1852 - 344 pages
...pentagons, (2) of regular octagons described within and about a circle. 188. The square of a side of the regular pentagon inscribed in a circle is equal to the square of a side of the inscribed hexagon, together with the square of a side of the inscribed decagon. 189.... | |
 | John Hind - Trigonometry - 1855 - 540 pages
...A BCD, whose angles Л, С are right angles : prove that the area = (»-a)(«-¿) = (*-u)(*-c). 4. The square of the side of a regular pentagon .inscribed in a circle, is equal to the sum of the squares of the sides of a regular hexagon and decagon, inscribed in the same circle. 5.... | |
| |